

Don't you want to read? Try listening to the article in audio mode 🎧
A Tag Manager, formally Tag Management System, is a platform that allows you to manage tags, a term used to indicate components also known as tracking pixels that are used in Digital Marketing to analyze the progress of advertising campaigns, obtain metrics useful to identify the target audience of a content, or carry out tests with which to evaluate the impact of different versions of the same online advertisement. Tags can be included on the pages of a website or in a web application in the form of code snippets, which is why they are also called tracking codes. A Tag Manager allows not only to generate them, but also to update and import them. There are several solutions of this kind, but only a few are as comprehensive as Google Tag Manager in terms of features. Let's analyze the characteristics of this tool by trying to understand what are the benefits from its implementation.
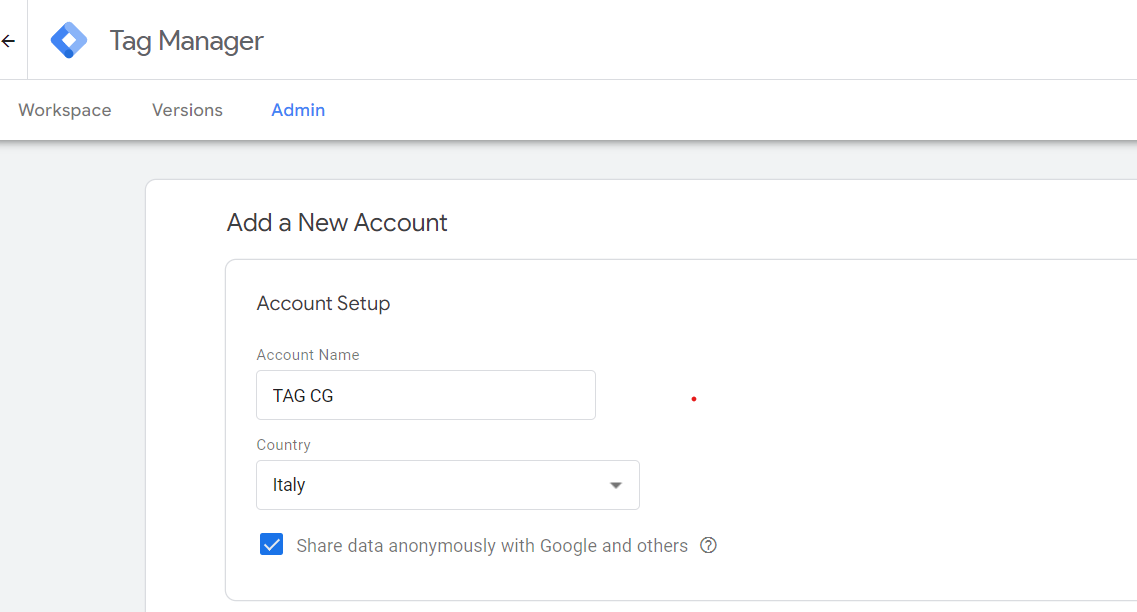 The phase that involves the generation of the tag container is also very simple. It is intended to provide a single space for the tags, regardless of whether they have been implemented through a service of the Google network or through third-party functionality. In this regard, it is good to remember that the tracking codes could be intended for specific platforms. For this reason, Google Tag Manager allows users to choose between the Web, the iOS and Android operating systems, AMPs (Accelerated Mobile Pages) and the use on the server side.
The phase that involves the generation of the tag container is also very simple. It is intended to provide a single space for the tags, regardless of whether they have been implemented through a service of the Google network or through third-party functionality. In this regard, it is good to remember that the tracking codes could be intended for specific platforms. For this reason, Google Tag Manager allows users to choose between the Web, the iOS and Android operating systems, AMPs (Accelerated Mobile Pages) and the use on the server side. 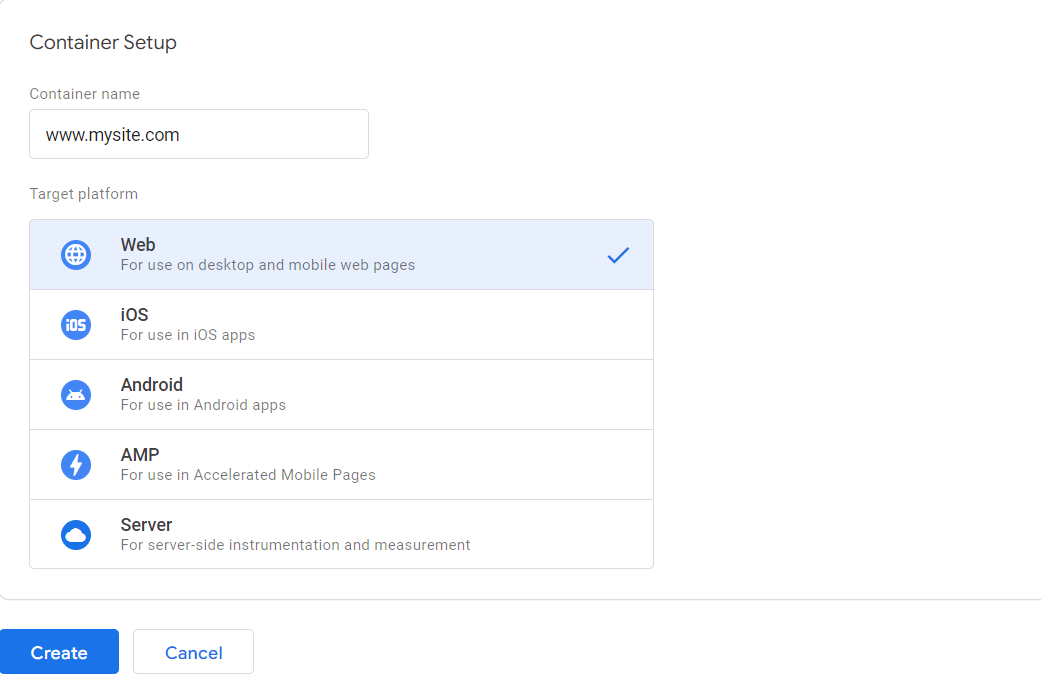 Once you have created the account and configured the container, you have the first, and perhaps most important, illustration of how Google Tag Manager allows you to carry out the greater part of operations without having to resort to the intervention of a developer. The codes to be included in the webpages are, in fact, generated quite automatically and they can be used immediately, by following the instructions provided by the system.
Once you have created the account and configured the container, you have the first, and perhaps most important, illustration of how Google Tag Manager allows you to carry out the greater part of operations without having to resort to the intervention of a developer. The codes to be included in the webpages are, in fact, generated quite automatically and they can be used immediately, by following the instructions provided by the system. 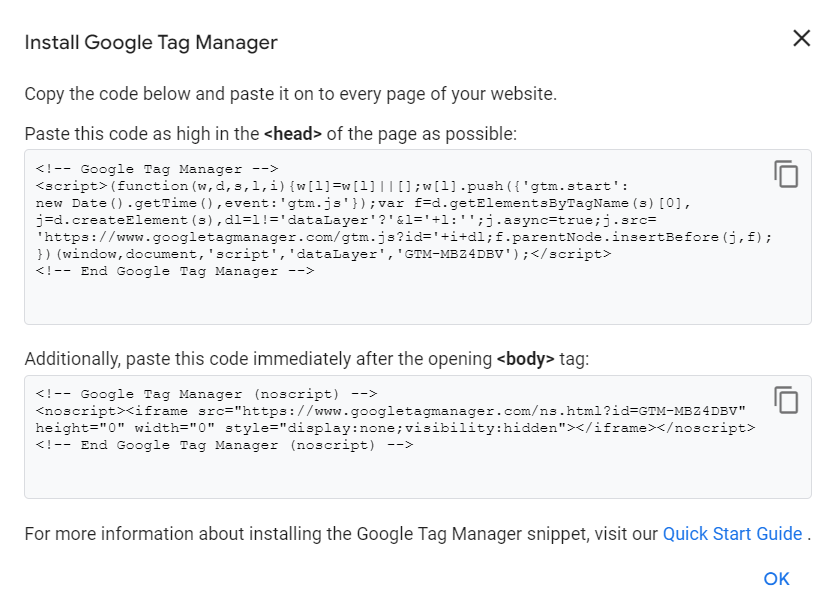 In a traditional workflow, those who have to manage tags for marketing purposes should turn to developers for all the phases that involve the creation of the tags, the passage from the definition of the triggers to the code creation that allows the activation of the tags through them, as well as for all functions that automate tag configuration and the objects that allow the transfer of information to the tags. With Google Tag Manager, on the other hand, it is the system that produces the codes necessary for the tracking pixels and their operation. This is true even in the event that the system is used for the use of tags related to other services. Google Tag Manager supports over 50 types of tags and you can also choose tag types based on custom HTML or custom images, as well as import ready-to-use tag templates from a gallery populated by the community itself of this service.
In a traditional workflow, those who have to manage tags for marketing purposes should turn to developers for all the phases that involve the creation of the tags, the passage from the definition of the triggers to the code creation that allows the activation of the tags through them, as well as for all functions that automate tag configuration and the objects that allow the transfer of information to the tags. With Google Tag Manager, on the other hand, it is the system that produces the codes necessary for the tracking pixels and their operation. This is true even in the event that the system is used for the use of tags related to other services. Google Tag Manager supports over 50 types of tags and you can also choose tag types based on custom HTML or custom images, as well as import ready-to-use tag templates from a gallery populated by the community itself of this service. 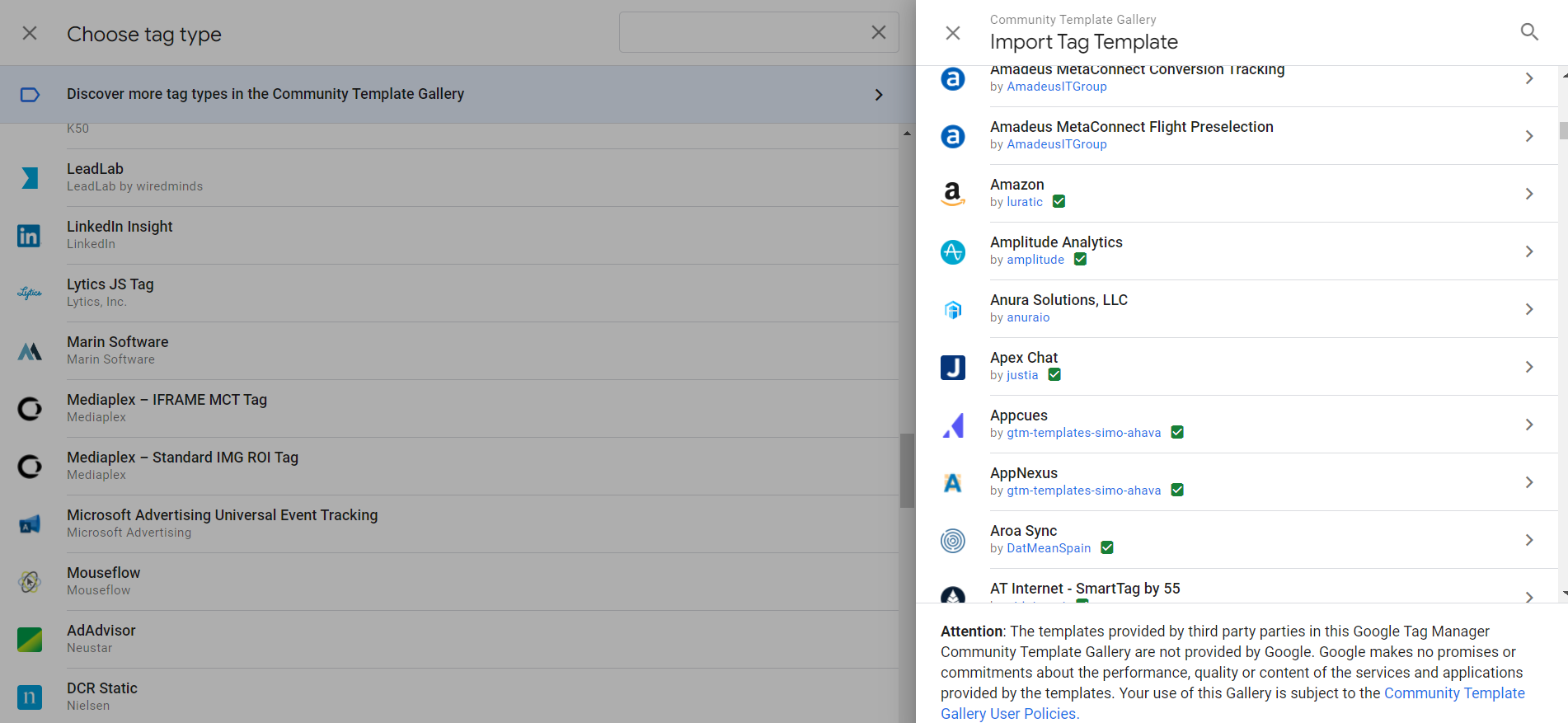 There is one last aspect that deserves to be highlighted: the relationship between the tags managed through Google Tag Manager and protection of privacy. As previously said, in fact, the purpose of this particular type of code is tracking. In this regard, the use of the platform has some benefits including integration with the CMP (Consent Management Platform) that enables users to use the tags in a manner consistent with the regulations regarding protection of personal data and consent to pixels and cookies. Google Tag Manager also has a special trigger, the Consent Initialization trigger designed to ensure that the consent settings are respected before any other trigger is fired. It is used for tags that set or update the user consent state for a specific website.
There is one last aspect that deserves to be highlighted: the relationship between the tags managed through Google Tag Manager and protection of privacy. As previously said, in fact, the purpose of this particular type of code is tracking. In this regard, the use of the platform has some benefits including integration with the CMP (Consent Management Platform) that enables users to use the tags in a manner consistent with the regulations regarding protection of personal data and consent to pixels and cookies. Google Tag Manager also has a special trigger, the Consent Initialization trigger designed to ensure that the consent settings are respected before any other trigger is fired. It is used for tags that set or update the user consent state for a specific website. 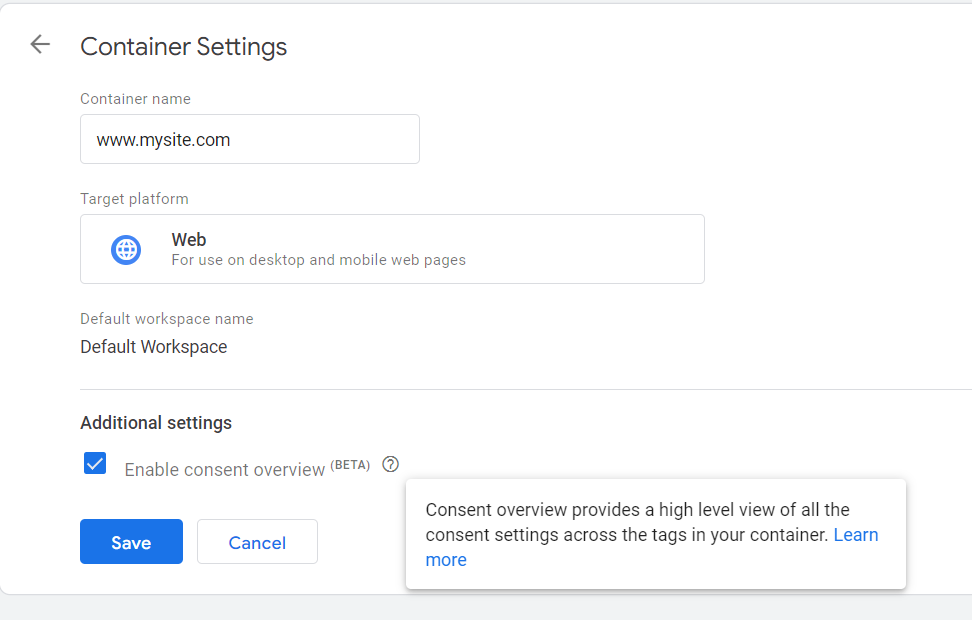 By default, all containers generated through Google Tag Manager include a Consent Initialization trigger for all pages on a website. Google Tag Manager, therefore, has become an essential tool for configuring tags. The intuitive interface has allowed many professionals, outside the world of coding, to create tags, triggers and variables, and the Preview and Debug mode has facilitated error correction without running the risk of losing crucial analytical data. Although the system is free of charge, it offers a very high level of performance and customization, suitable for both newbie and advanced users.
By default, all containers generated through Google Tag Manager include a Consent Initialization trigger for all pages on a website. Google Tag Manager, therefore, has become an essential tool for configuring tags. The intuitive interface has allowed many professionals, outside the world of coding, to create tags, triggers and variables, and the Preview and Debug mode has facilitated error correction without running the risk of losing crucial analytical data. Although the system is free of charge, it offers a very high level of performance and customization, suitable for both newbie and advanced users.
Screenshot by Google.com
Why use Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is a completely free service that is based on a very easy-to-use system for tag implementation and configuration. Among its main advantages, first of all, is that of having a centralized interface through which it is possible to manage all the tracking codes of your online marketing campaigns. Another main feature of this platform concerns the fact that it guarantees a partial degree of independence from IT. In fact, Google Tag Manager can also be used by professionals other than developers, such as those who work in the field of SEO (Search Engine Optimization), as it significantly reduces the number of operations related to coding. This is possible thanks to the container tags, that is tag sets involving configurations and variables of the latter, and replacing the manually generated tags, be it of third parties (Facebook Ads, LinkedIn Ads…) or associated with other Mountain View’s services, with which Google Tag Manager is integrated, such as Google Ads, Floodlight and Google Analytics. The platform does not only have benefits, this is because any inclusion of code capable of determining interactions with external servers can result in longer loading times for web pages. That is why it is therefore a good idea to use Google Tag Manager, always carefully checking its impact on performances.How does Google Tag Manager work
On a technical level, Google Tag Manager provides for the insertion of a snippet, that is the portion of JavaScript code that allows tracking of the target webpage within the HTML code. To do this, you must first have access to the source of web pages. The service involves the creation of an account through which to manage Google Tag Manager’s building blocks which are, in the following order:- tags, that is the tracking codes;
- triggers that allow the activation of tags, in correspondence of specific events;
- variables or additional functions associated with tags that simplify and automate the configuration procedures;
- the data layer, that is the object used by Google Tag Manager to pass information to the tags.
How to speed up and simplify my daily task
Compared to the classic tag implementation system that sees the work of the marketing division strictly dependent on the work of the developers, the advantages deriving from the use of Google Tag Manager are immediately evident, as soon as the service is activated. In fact, to start using the platform, simply create a new account, associate a name and decide the area in which the tracking activity will be carried out, for example Italy. Optionally, it is possible to share the data generated through the account with Google and third-party services. This information will be stripped off of all references that could be used to identify a website, and will be employed anonymously to carry out benchmarks aimed at improving performance. The phase that involves the generation of the tag container is also very simple. It is intended to provide a single space for the tags, regardless of whether they have been implemented through a service of the Google network or through third-party functionality. In this regard, it is good to remember that the tracking codes could be intended for specific platforms. For this reason, Google Tag Manager allows users to choose between the Web, the iOS and Android operating systems, AMPs (Accelerated Mobile Pages) and the use on the server side.
The phase that involves the generation of the tag container is also very simple. It is intended to provide a single space for the tags, regardless of whether they have been implemented through a service of the Google network or through third-party functionality. In this regard, it is good to remember that the tracking codes could be intended for specific platforms. For this reason, Google Tag Manager allows users to choose between the Web, the iOS and Android operating systems, AMPs (Accelerated Mobile Pages) and the use on the server side.  Once you have created the account and configured the container, you have the first, and perhaps most important, illustration of how Google Tag Manager allows you to carry out the greater part of operations without having to resort to the intervention of a developer. The codes to be included in the webpages are, in fact, generated quite automatically and they can be used immediately, by following the instructions provided by the system.
Once you have created the account and configured the container, you have the first, and perhaps most important, illustration of how Google Tag Manager allows you to carry out the greater part of operations without having to resort to the intervention of a developer. The codes to be included in the webpages are, in fact, generated quite automatically and they can be used immediately, by following the instructions provided by the system.  In a traditional workflow, those who have to manage tags for marketing purposes should turn to developers for all the phases that involve the creation of the tags, the passage from the definition of the triggers to the code creation that allows the activation of the tags through them, as well as for all functions that automate tag configuration and the objects that allow the transfer of information to the tags. With Google Tag Manager, on the other hand, it is the system that produces the codes necessary for the tracking pixels and their operation. This is true even in the event that the system is used for the use of tags related to other services. Google Tag Manager supports over 50 types of tags and you can also choose tag types based on custom HTML or custom images, as well as import ready-to-use tag templates from a gallery populated by the community itself of this service.
In a traditional workflow, those who have to manage tags for marketing purposes should turn to developers for all the phases that involve the creation of the tags, the passage from the definition of the triggers to the code creation that allows the activation of the tags through them, as well as for all functions that automate tag configuration and the objects that allow the transfer of information to the tags. With Google Tag Manager, on the other hand, it is the system that produces the codes necessary for the tracking pixels and their operation. This is true even in the event that the system is used for the use of tags related to other services. Google Tag Manager supports over 50 types of tags and you can also choose tag types based on custom HTML or custom images, as well as import ready-to-use tag templates from a gallery populated by the community itself of this service.  There is one last aspect that deserves to be highlighted: the relationship between the tags managed through Google Tag Manager and protection of privacy. As previously said, in fact, the purpose of this particular type of code is tracking. In this regard, the use of the platform has some benefits including integration with the CMP (Consent Management Platform) that enables users to use the tags in a manner consistent with the regulations regarding protection of personal data and consent to pixels and cookies. Google Tag Manager also has a special trigger, the Consent Initialization trigger designed to ensure that the consent settings are respected before any other trigger is fired. It is used for tags that set or update the user consent state for a specific website.
There is one last aspect that deserves to be highlighted: the relationship between the tags managed through Google Tag Manager and protection of privacy. As previously said, in fact, the purpose of this particular type of code is tracking. In this regard, the use of the platform has some benefits including integration with the CMP (Consent Management Platform) that enables users to use the tags in a manner consistent with the regulations regarding protection of personal data and consent to pixels and cookies. Google Tag Manager also has a special trigger, the Consent Initialization trigger designed to ensure that the consent settings are respected before any other trigger is fired. It is used for tags that set or update the user consent state for a specific website.  By default, all containers generated through Google Tag Manager include a Consent Initialization trigger for all pages on a website. Google Tag Manager, therefore, has become an essential tool for configuring tags. The intuitive interface has allowed many professionals, outside the world of coding, to create tags, triggers and variables, and the Preview and Debug mode has facilitated error correction without running the risk of losing crucial analytical data. Although the system is free of charge, it offers a very high level of performance and customization, suitable for both newbie and advanced users.
By default, all containers generated through Google Tag Manager include a Consent Initialization trigger for all pages on a website. Google Tag Manager, therefore, has become an essential tool for configuring tags. The intuitive interface has allowed many professionals, outside the world of coding, to create tags, triggers and variables, and the Preview and Debug mode has facilitated error correction without running the risk of losing crucial analytical data. Although the system is free of charge, it offers a very high level of performance and customization, suitable for both newbie and advanced users. Screenshot by Google.com
Article updated on: 14 August 2023

Don't Waste Your Talent. Turn It Into a Career With a Course That Fits Your Needs!
Talent Garden is your Digital Skills Academy, offering courses in Digital Marketing, UX Design, Digital HR and Data Analysis designed to launch your career.
Keep reading

4
min read
How to become a Chief Risk Officer (or Risk Manager)
What is Risk Management: the definition Risk management is a task that includes all identification processes, ...
Talent Garden
04/03/2022

7
min read
What is Project Management: How much does it earn and what does a Project Manager do?
Only a few job roles are as truly versatile as a Project Manager. Not only is Project Management needed in an array of ...
Talent Garden
22/07/2020

2
min read
CheckVentory, the vehicle auditing solution that works for every business
CheckVentory is a Dublin based startup helping businesses take control of their inventory and manage it all from a ...
Talent Garden
18/08/2018

4
min read
What Project Managers do, how to become one and how much they earn
Nowadays companies, whether large or medium-small, or even startups, are increasingly resorting to project management ...
Talent Garden
12/05/2022
