

Don't you want to read? Try listening to the article in audio mode 🎧
Danish computer scientist Jakob Nielsen, who is considered one of the world's foremost authorities in terms of usability, defines the latter as the metric that allows you to assess the quality of users’ experience when interacting with something.
A tool with which users can operate is therefore considered usable when it proves to be intuitive, easy to remember, guarantees an enjoyable user experience, has a high level of efficiency and gives rise to few errors when interacting with it.
Nielsen's definition is shared by the US computer scientist Ben Shneiderman who is also responsible for some fundamental research on ergonomics, and therefore the interaction between human and machine. In fact, he has identified four dimensions related to the concept of usability:
 To do this, a rational content layout has been chosen, which is easily usable through a main menu with which to quickly access sections and subsections, also allowing you to translate the website into all supported languages and to access all important topics with a single click.
Another example of usability is provided by the Airbnb website, a well-known platform available to those looking for accommodation online. The portal, which shows the work done to optimize the user experience on mobile devices, presents a well-studied balance between images and content. All sections are adequately highlighted to ensure immediate availability.
To do this, a rational content layout has been chosen, which is easily usable through a main menu with which to quickly access sections and subsections, also allowing you to translate the website into all supported languages and to access all important topics with a single click.
Another example of usability is provided by the Airbnb website, a well-known platform available to those looking for accommodation online. The portal, which shows the work done to optimize the user experience on mobile devices, presents a well-studied balance between images and content. All sections are adequately highlighted to ensure immediate availability. 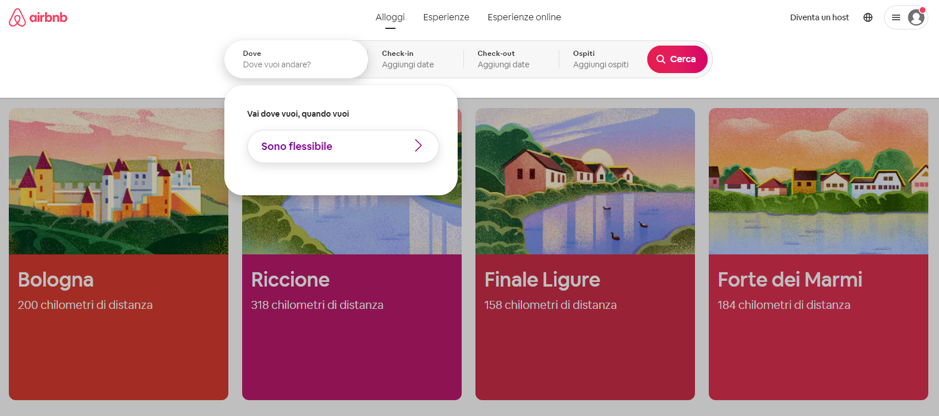 In this regard, it is useful to note how the accommodation search system has been organized, with a form that requires little essential information in order to speed up the transition from request to obtaining results as early as possible.
In this regard, it is useful to note how the accommodation search system has been organized, with a form that requires little essential information in order to speed up the transition from request to obtaining results as early as possible.
- efficiency: that is the ability of a tool to respond to the purpose for which it was created;
- learnability: the ease of learning associated with the use of a tool and its features;
- memorability: the ease of remembering the main commands for using a tool;
- satisfaction: the satisfaction that a tool is able to generate during its use.
Website usability: definition
When dealing with website usability, it is good to take into account the feature that unmistakably distinguishes this particular tool from other products. In fact, in most cases a product is used after it has been purchased, while a website is used immediately, and if the user experience is satisfactory, it can give rise to behaviors, such as the execution of an order, the subscription to a service or the click on an advertisement, which allow the website itself to increase monetization. What are the criteria for establishing whether a website is usable or not? Susan M. Dray, known for her work on UX (user experience) and HCI (human–computer interaction), argues that a tool cannot be considered functional if users fail to use it. By applying this concept to the Internet, it is possible to consider a website usable if it allows you to access the information, features or services you are looking for, even when you visit it for the first time. An e-commerce platform in which users cannot find the product they need (even if present), require operator assistance to make a purchase, do not find useful references to get help when they need it, or must carry out a cumbersome procedure to make an order, cannot be classified as a usable website. The concept of usability should not be confused with that of accessibility, partly taking up the definition given by the AGID (Agenzia per l'Italia Digitale, that is Agency for Digital Italy). Accessibility is in fact the ability to provide services and information that can also be used by those who, due to disabilities, need assistive technologies or particular configurations. It is therefore easy to understand that a website can be considered accessible when it is also usable.The main features of a usable website
To create a usable website, end users must be the reference point of its design, and this means to identify with their needs during development, taking into account the feedback recorded in the testing phase and, once in production, to assess the relevance of the feedback received with a view to continuous integration. Various factors are involved in the usability of a website, starting with its structure. The organization of the content must in fact be consistent and such to facilitate availability thereof. To do this, the website must be, first and foremost, easy to navigate, with a menu that effectively represents the hierarchy of the proposed sections. In the same way, the individual contents and the relationships between them must be clear and easy to consult, for example titles and subtitles contribute to these aspects, as well as the links that connect the various pages or that allow to anchor the different components of the same page, as happens with summaries, for example. It is also essential not to underestimate the features that allow the interaction between the user and the website. Each procedure must in fact be designed in order to be faced autonomously, avoiding all those elements that could increase its complexity without offering a real advantage in terms of use. Furthermore, among the elements that contribute to usability are the chosen layout, the text readability - where fonts, size and the contrast to backgrounds have a relevant role - as well as the quality of the images, which must be consistent with the topics covered and with the graphics settings used. It should not be forgotten that a usable website is also a responsive website, which allows you to browse on multiple devices without losing quality in terms of user experience, as well as performance. Long loading times of the pages in fact result in a low degree of satisfaction of users. These are just a few of the features that make a website usable, by harmonizing presentation, content and functionality. In fact, a professional approach to this subject requires in-depth preparation and a specific training course. That is why Talent Garden offers a UX Design Master, the only one in Italy that enables you to become a Junior UX Designer in just 14 weeks. The master course is organized in collaboration with Sketchin, one of the most successful design studios in Europe. Thanks to the partnership with the Pantheon Design & Technology Institute, the master course also guarantees the recognition of 24 academic/university formative credits. The next edition of the UX Design Master will take place in blended learning mode starting from 19th September 2022 and, in addition to 11 weeks of live online lessons, the 1st, 4th and 8th week will be in presence in the Milan and Rome Campuses. Participants can choose the city of their interest to attend the course.Examples of usable websites for users
As we would like to propose an example of usability applied to the Internet, it is worth highlighting the good work done for the creation of the official website of Emergency, an Italian humanitarian association operating all over the world. Its pages have the dual intent of describing the organization's activities and collecting donations. To do this, a rational content layout has been chosen, which is easily usable through a main menu with which to quickly access sections and subsections, also allowing you to translate the website into all supported languages and to access all important topics with a single click.
Another example of usability is provided by the Airbnb website, a well-known platform available to those looking for accommodation online. The portal, which shows the work done to optimize the user experience on mobile devices, presents a well-studied balance between images and content. All sections are adequately highlighted to ensure immediate availability.
To do this, a rational content layout has been chosen, which is easily usable through a main menu with which to quickly access sections and subsections, also allowing you to translate the website into all supported languages and to access all important topics with a single click.
Another example of usability is provided by the Airbnb website, a well-known platform available to those looking for accommodation online. The portal, which shows the work done to optimize the user experience on mobile devices, presents a well-studied balance between images and content. All sections are adequately highlighted to ensure immediate availability.  In this regard, it is useful to note how the accommodation search system has been organized, with a form that requires little essential information in order to speed up the transition from request to obtaining results as early as possible.
In this regard, it is useful to note how the accommodation search system has been organized, with a form that requires little essential information in order to speed up the transition from request to obtaining results as early as possible.
Conclusions
Website usability is a quality attribute that allows you to maximize the quality of the user experience while browsing. To obtain it, it is necessary to take into account end users’ demands, trying to understand their needs, expectations and which features a website must have in order to ensure satisfaction and engender loyalty. A usable website is also capable of generating more traffic and encouraging conversions. To obtain these results, however, it is crucial to understand how the structure, content and functionality for the interaction can improve the user experience.
Article updated on: 09 August 2023

Don't Waste Your Talent. Turn It Into a Career With a Course That Fits Your Needs!
Talent Garden is your Digital Skills Academy, offering courses in Digital Marketing, UX Design, Digital HR and Data Analysis designed to launch your career.
Keep reading

6
min read
The best UX Design apps: 5 tools that will make your life easier
User Experience Design (hereinafter “UX Design”) is a process aimed at making a user interface usable and pleasing. In ...
Talent Garden
14/03/2022

2
min read
Meet our Community: Tommaso Bussoletti, UI & UX Designer at Cerved Group
“Believe in what you want to do.” Tommaso Bussoletti UI/UX Designer at Cerved Group and Talent Garden Innovation School ...
Talent Garden
08/12/2019
7
min read
10 Ways to Utilize User Experience Analytics to Improve Website Engagement
What does the term user experience analytics mean? Why is it a useful tool? And how can you utilize it to improve ...
Talent Garden
31/01/2023

2
min read
What does a human resources manager do
While some of their work may be less visible than others, the human resources manager is a fundamental element of a ...
Talent Garden
18/05/2021
